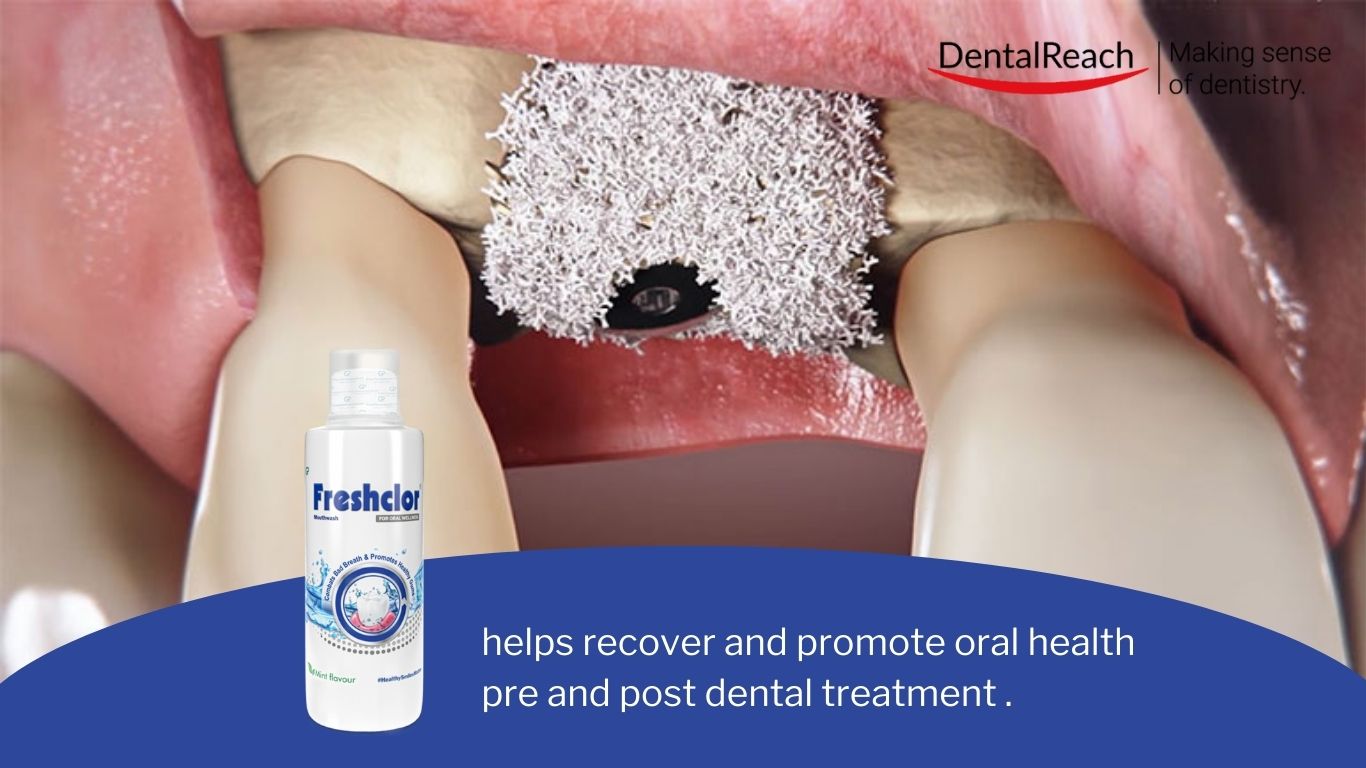
Guided bone regeneration (GBR) is a usually used process for regenerating bone defects, ceaselessly hired in dental surgical procedures. This find out about aimed to analyze the adherence of Candida albicans on six commercially to be had polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) membranes utilized in GBR procedures and to grasp the medical implications of such adherence.
Fabrics and Strategies
The find out about evaluated six PTFE membranes: two with textured surfaces and 4 with non-textured surfaces. C. albicans (ATCC 24433) was once cultured for twenty-four hours, and its cellular floor hydrophobicity was once assessed the usage of a changed means. The adhesion of C. albicans to membrane discs was once analyzed the usage of scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and real-time polymerase chain response (PCR).
Effects
- albicans exhibited important hydrophobicity at 77.25%. SEM research printed patchy, scattered, and small clustered patterns of C. albicans adherence throughout all membranes except for for one non-textured membrane with a coarse floor the place a thick biofilm shaped. Actual-time PCR quantification confirmed considerably upper adhesion ranges on PTFE membranes in comparison to regulate membranes (p ≤. 001). Textured surfaces had the perfect depend of adhered cells at 2680 × 10^4 cells/ml in comparison to non-textured surfaces at 707 × 10^4 cells/ml (p ≤. 001). One specific rough-surfaced non-textured membrane exhibited the perfect depend at 3010 × 10^4 cells/ml (p ≤. 05).
The knowledge indicated that floor texture and roughness considerably affect C. albicans adherence to PTFE membranes utilized in GBR procedures.
Textured PTFE membranes demonstrated upper counts of adhered fungal cells because of their hexagonal-shaped indentations which facilitate cellular adhesion but additionally cause them to extra vulnerable to microbial contamination.
What are the Medical Penalties of Such Adherence?
The colonization through C. albicans on uncovered PTFE membranes can result in biofilm formation along different oral microorganisms, probably inflicting irritation in surrounding cushy tissues, contributing to oral candidiasis, or serving as reservoirs for periodontal pathogen recolonization.
Research have proven that microbial infections following membrane publicity can necessitate early elimination of those limitations, complicating postoperative results through permitting verbal exchange between the oral surroundings and newly forming tissues—thereby expanding an infection dangers.
- albicans interacts synergistically with quite a lot of bacterial species inside of polymicrobial biofilms, improving virulence elements comparable to antibiotic resistance and pathogenicity in sicknesses like periodontitis and peri-implantitis.
Hydrophobic interactions play a a very powerful position in microbial attachment; organisms like C. albicans adhere strongly to hydrophobic surfaces like PTFE because of their inherent hydrophobic homes.
This find out about highlights that the stage of floor roughness and texture considerably impacts C. albicans adhesion on PTFE membranes utilized in GBR procedures. Those findings can have an effect on the surgeon’s collection of GBR membrane and postoperative repairs.
Long term analysis must discover methods for editing membrane surfaces or growing antimicrobial coatings that might cut back microbial colonization whilst keeping up their regenerative efficacy.
Supply: Magazine of Medical and Experimental Dental Analysis
Learn the entire article right here: https://doi.org/10.1002/cre2.902